Detecting heap integrity violations
Description
Checks for various heap integrity violations. The check can either be manually triggered or can be set up to be triggered at regular intervals of use of the heap interface. Integrity problems that can be detected when you enable this check are:
Destruction of the internal heap structure. Mostly, this is because a write access through a pointer expression is incorrect. Use out-of-bounds checking to try to locate the erroneous write access.
Write accesses outside allocated memory, for example:
char * p = (char *)malloc(100); /* Memory is allocated. */ ... p[100] = ... /* This write access is out of bounds. */
A write access that is out-of-bounds of the heap block and that changes the guards in front of or after the heap block will be detected. Any other write accesses will not be detected.
Write accesses to freed memory, for example:
char * p = (char *)malloc(...); /* Memory is allocated. */ ... free(p); /* Memory is freed. */ ... p[...] = ... /* Write access to freed memory. */
If the memory that contains the original
pis allocated again beforepis written to, this error will typically not be detected. By using the delayed free list (see below), this error can be found.
Why perform the check
Use the checked heap if you suspect that your application, at some point, writes erroneously in the heap, for example by misusing a heap block.
How to use it
Linker option: ‑‑debug_heap
In the IDE: Project>Options>Runtime Checking>Use checked heap
The checked heap will replace the normal heap for the whole application. The checked heap requires extra heap and stack resources. Make sure that your application has at least 10 Kbytes of heap and 4 Kbytes of stack.
For detecting heap integrity violations, you can use these functions which are defined in iar_dlmalloc.h:
size_t __iar_check_heap_integrity(void);Use this function to verify the integrity of the heap. If any corruptions are detected, they are reported. The return value is the number of found problems. There is a limit on the number of corruption errors that are reported. This limit can be changed by using the
__iar_set_integrity_report_limitfunction. Execution is only stopped when the final message is generated. The default number of reported messages is 10. A call to__iar_check_heap_integrityis not guaranteed to return to the caller if the heap is corrupt.size_t __iar_set_heap_check_frequency(size_t interval);Use this function to specify how often the periodic heap integrity checks are performed. By default, the periodic checks are turned off (
interval= 0). Ifintervalis a positive number, the integrity will be checked everyinterval:th heap operation where every call tofree/malloc/new/delete/realloc/etc counts as one operation. The function returns the old interval, which means that the state can be restored if necessary. The heap check interval can be increased or turned off when trusted parts of your application program, and then be decreased when you run parts of your application that are likely to contain heap errors.size_t __iar_set_delayed_free_size(size_t size);Use this function to specify the maximum size of the freed delay list. By default, the freed delay list is turned off (
size= 0). This function has no effect on the actual size of the list, it only changes the maximum. The function returns the previous value so it can be restored if necessary.The freed delay list can be used to try to find locations in your application that use a freed heap block. This can help you detect:
Mixing up an old heap block pointer that has been freed with a new, freshly allocated heap block pointer. Because the freed delay list will delay the actual reuse of a freed heap block, the behavior of your application might change and you might be able to detect the presence of this kind of problem.
Writes to already freed heap blocks. If a heap block is in the freed delay list, it will get specific content, different from when it is actually freed, and a heap integrity check can find those erroneous write accesses to the heap block.
size_t __iar_free_delayed_free_size(size_t count);Use this function to make sure that at most
countelements are present in the freed delay list. Superfluous elements are freed (the oldest ones change first). It has no effect on the maximum size of the list—it only changes the current number of elements. Calling this function has no effect ifcountis larger than the current size of the list. The function returns the number of freed elements.
How it works
The checked heap will replace the normal heap for the whole application.
The freed delay list is a queuing mechanism for free calls. When calling free, or an equivalent memory operation that returns memory to the heap, the recently freed pointer is queued to be freed instead of actually being freed. If the maximum size of the delay list is exceeded, the oldest elements above the maximum size in the freed delay list are actually freed.
All errors that the checked heap reports, mention a heap block that is somehow corrupt. The checked heap cannot inform about who corrupted the heap block or when it was corrupted. You can use calls to the __iar_debug_check_heap_integrity function to verify the integrity during application execution and narrow down the list of potential candidates.
For example:
... __iar_debug_check_heap_integrity(); /* Pre-check */ my_function(..., ..., ...); __iar_debug_check_heap_integrity(); /* Post-check */ ...
If the post-check reports problems that the pre-check does not, it is probable that my_function corrupted the heap.
The checked heap consumes resources:
The checked heap requires more ROM space than the normal heap implementation
All heap operations require more time in the checked heap
Each heap block in the checked heap contains additional space for bookkeeping, which results in increased RAM usage for your application.
See The checked heap provided by the library.
Example
Follow the procedure described in Getting started using C-RUN runtime error checking, but use the Checked heap option.
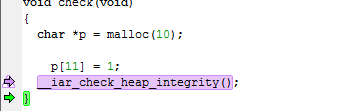
This is an example of source code that will be identified during runtime:
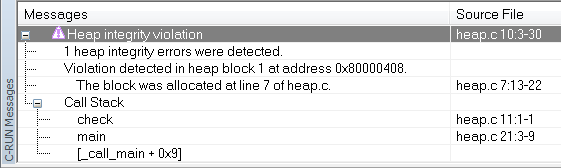
C-RUN will report Heap integrity violation. This is an example of the message information that will be listed: