Target options
The Target options specify target-specific features for the IAR C/C++ Compiler and Assembler.
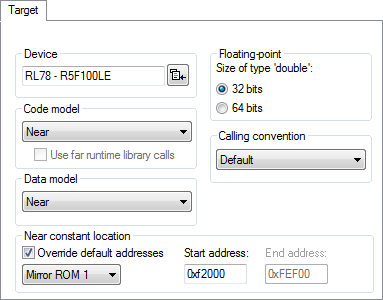
Device
The device your are using. The choice of device will automatically determine the default linker configuration file and C-SPY® device description file. For information about how to override the default files, see the C-SPY Debugging documentation.
Code model
Selects the code model for your project. Choose between:
For more information about the code models, see Code models and memory attributes for function storage.
Use far runtime library calls
Places the runtime library support routines in __far_func memory. This option can be used for moving the support routines from near to far memory when building a customized library. Note that the startup code will still be located in near memory.
Data model
Selects the data model for your project. Choose between:
For more information about the data models, see Data models.
Near constant location
Specify the location for __near-declared constants and strings:
- Override default addresses
Makes it possible to override the default start and end addresses for where in the RAM the constants shall be placed.
- Copy to RAM
Constants are located in RAM, in the range
0xF0000–0xFFFFF
- Mirror ROM0
Constants are located in ROM, in the range
0x00000–0x0FFFF, and are mirrored by hardware to RAM, in the range0xF0000–0xFFFFF
- Mirror ROM1
Constants are located in ROM, in the range
0x10000–0x1FFFF, and are mirrored by hardware to RAM, in the range0xF0000–0xFFFFF
- Start address
Type an address to override the default start address for where in the RAM the constants shall be placed.
- End address
Type an address to override the default end address for where in the RAM the constants shall be placed.
For information about how this works and the available memory ranges, see the chip manufacturer’s documentation.
Floating-point
The compiler represents floating-point values by 32- and 64-bit numbers in standard IEEE 754 format. Size of type 'double' selects the size of the type double. Choose between:
For more information about the floating-point format, see Basic data types—floating-point types.
Calling convention
Selects the calling convention for your project. Choose from:
For more information about the calling conventions, see Choosing a calling convention.