- IAR Embedded Workbench for RL78 5.20
- IDE Project Management and Building
- The development environment
- Reference information on the IDE
- Configure Custom Argument Variables dialog box
Configure Custom Argument Variables dialog box
What do you want to do?
Get a list of predefined argument variables: Argument variables
Get reference information about the Configure Custom Argument Variables dialog box, see below the line.

The Configure Custom Argument Variables dialog box is available from the Tools menu.
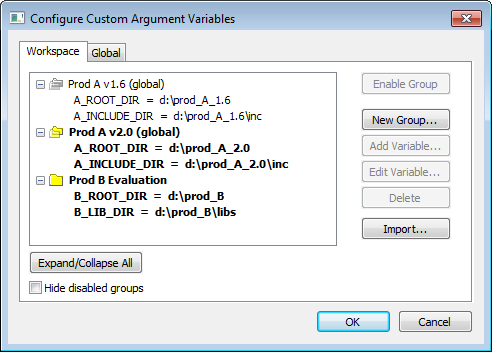
Use this dialog box to define and edit your own custom argument variables. Typically, this can be useful if you install a third-party product and want to specify its include directory by using argument variables. Custom argument variables can also be used for simplifying references to files that you want to be part of your project.
Custom argument variables have one of two different scopes:
Workspace-local variables, which are associated with a specific workspace and can only be seen by the workspace that was loaded when the variables were created.
Global variables, which are available for use in all workspaces
You can organize your variables in named groups.
Workspace and Global tabs
Click the tab with the scope you want for your variable:
- Workspace
Both global and workspace-local variables are visible in the display area.
Only workspace-local variables can be edited or removed.
Groups of variables as well as individual variables can be added or imported to the local level.
Workspace-local variables are stored in the file
Workspace.custom_argvarsin a specific directory, see Files for local settings.
- Global
Only variables that are defined as global are visible in the display area—all these variables can be edited or removed.
Groups of variables as well as individual variables can be added or imported to the global level.
Global variables are stored in the file
global.custom_argvarsin a specific directory, see Files for global settings.
Warning
Note that when you rely on custom argument variables in the build tool settings, some of the information needed for a project to build properly might now be in a .custom_argvars file. You should therefore consider version-controlling your custom argument file (workspace-local and global), and whether to document the need for using these variables.
Expand/Collapse All
Expands or collapses the view of the variables.
Hide disabled groups
Hides all groups of variables that you previously have disabled.
Enable Group / Disable Group
Enables or disables a group of variables that you have selected. The result differs depending on which tab you have open:
Workspace tab—Enabling or disabling groups will only affect the current workspace.
Global tab—Enabling will only affect newly created workspaces. These will inherit the current global state as the default for the workspace.
Note
You cannot use a variable that is part of a disabled group.
New Group
Opens the New Group dialog box where you can specify a name for a new group. When you click OK, the group is created and appears in the list of custom argument variables.
Add Variable
Opens the Add Variables dialog box where you can specify a name and value of a new variable to the group you have selected. When you click OK, the variable is created and appears in the list of custom argument variables.
Note that you can also add variables by importing previously defined variables. See Import below.
Edit Variable
Opens the Edit Variables dialog box where you can edit the name and value of a selected variable. When you click OK, the variable is created and appears in the list of custom argument variables.
Delete
Deletes the selected group or variable.
Import
Opens a file browser where you can locate a Workspace.custom_argvars file. The file can contain variables already defined and associated with another workspace or be a file created when installing a third-party product.