Checksum
The Checksum options control filling and checksumming.
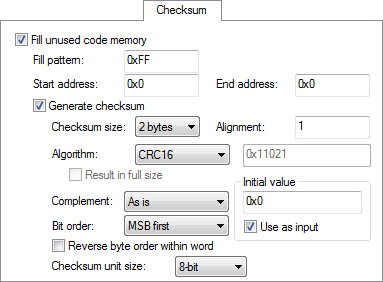
For more information about checksum calculation, see Checksum calculation for verifying image integrity.
Fill unused code memory
Fills unused memory in the range you specify. Choose between:
- Fill pattern
Specifies a size, in hexadecimal notation, of the filler to be used in gaps between segment parts.
- Start address
Specifies the start address for the range to be filled.
- End address
Specifies the end address for the range to be filled.
Generate checksum
Generates a checksum for the specified range. Choose between:
- Checksum size
Selects the size of the checksum, which can be 1, 2, 4, or 8 bytes.
- Alignment
Specifies an optional alignment for the checksum. Typically, this is useful when the processor cannot access unaligned data. If you do not specify an alignment explicitly, an alignment of 1 is used.
- Algorithm
Selects the algorithm to be used when calculating the checksum. Choose between:
Arithmetic sum, the simple arithmetic sum algorithm. The result is truncated to one byte.
CRC16 (default), the CRC16 algorithm (generating polynomial 0x1021).
CRC32, the CRC32 algorithm (generating polynomial 0x4C11DB7).
CRC polynomial, the CRC polynomial algorithm, a generating polynomial of the value you specify.
CRC64ISO, the CRC64ISO algorithm (generating polynomial 0x1B).
CRC64ECMA, the CRC64ECMA algorithm (generating polynomial 0x42F0E1EBA9EA3693).
Sum32, a word-wise (32 bits) calculated arithmetic sum.
- Result in full size
Generates the result of the arithmetic sum algorithm in the size you specify instead of truncating it to one byte.
- Complement
Selects the complement variant. Leave either as is, or select the one’s complement or two’s complement.
- Bit order
Selects the order in which the bits in each byte will be processed. Choose between:
MSB first, outputs the most significant bit first for each byte.
LSB first, reverses the bit order for each byte and outputs the least significant bit first.
- Reverse byte order within word
Reverses the byte order of the input data within each word of the size specified in Checksum unit size.
- Initial value
Specifies an initial value for the checksum. This is useful if the microcontroller you are using has its own checksum calculation and you want that calculation to correspond to the calculation performed by the linker.
- Use as input
Prefixes the input data with a word of size Checksum unit size that contains the value specified in Initial value.
- Checksum unit size
Selects the size of the unit for which a checksum should be calculated. Typically, this is useful to make the linker produce the same checksum as some hardware CRC implementations that calculate a checksum for more than 8 bits per iteration. Choose between:
8-bit, calculates a checksum for 8 bits in every iteration.
16-bit, calculates a checksum for 16 bits in every iteration.
32-bit, calculates a checksum for 32 bits in every iteration.
64-bit, calculates a checksum for 64 bits in every iteration.