Trace window
What do you want to do?
Learn about:
Learn how to:
Get reference information about the Trace window, see below the line.

The Trace window is available from the C-SPY driver menu.
This window displays the collected trace data.
Note
There are three different trace windows—ETM Trace, SWO Trace, and just Trace for the C-SPY simulator. The windows look slightly different.
The contents of the Tracewindow depend on the C-SPY driver you are using and the trace support of your debug probe.
Requirements
One of these alternatives:
The C-SPY Simulator. (Not available for all cores and devices.)
A CMSIS-DAP probe
An I-jet or I-jet Trace in-circuit debugging probe
A J-Link/J-Trace JTAG/SWD probe
An ST-LINK JTAG/SWD probe
A TI XDS probe
Trace toolbar
The toolbar in the Trace window contains:
- Enable/Disable
Enables and disables collecting and viewing trace data in this window.
- Clear trace data
Clears the trace buffer. Both the Trace window and the Function Trace window are cleared.
- Toggle source

Toggles the Trace column between showing only disassembly or disassembly together with the corresponding source code.
- Browse

Toggles browse mode on or off for a selected item in the Trace window, see Browsing through trace data.
- Find

Displays a dialog box where you can perform a search, see Find in Trace dialog box.
- Save

In the ETM Trace and SWO Trace windows, this button displays the Trace Save dialog box, see Trace Save dialog box.
In the C-SPY I-jet driver and in the C-SPY simulator, this button displays a standard Save As dialog box where you can save the collected trace data to a text file, with tab-separated columns.
- Edit Settings

In the C-SPY simulator, this button is not enabled.
In the ETM Trace window this button displays the Trace Settings dialog box, see ETM Trace Settings dialog box (J-Link/J-Trace) and ETM Trace Settings dialog box (I-jet).
In the SWO Trace window this button displays the SWO Trace Window Settings dialog box, see SWO Trace Window Settings dialog box.
- Progress bar

When a large amount of trace data has been collected, there might be a delay before all of it has been processed and can be displayed. The progress bar reflects that processing.
Display area (in the C-SPY simulator)
This area displays a collected sequence of executed machine instructions. In addition, the window can display trace data.
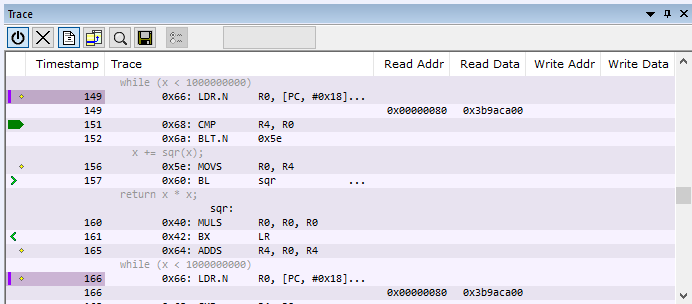
This area contains these columns for the C-SPY simulator:
The leftmost column contains identifying icons to simplify navigation within the buffer:

The yellow diamond indicates the trace execution point, marking when target execution has started.
The right green arrow indicates a call instruction.

The left green arrow indicates a return instruction.

The dark green bookmark indicates a navigation bookmark.

The red arrow indicates an interrupt.

The violet bar indicates the results of a search.
- Timestamp
The number of cycles elapsed to this point.
- Trace
The collected sequence of executed machine instructions. Optionally, the corresponding source code can also be displayed.
- Read Addr, Read Data, Write Addr, Write Data
These columns show reads and writes to memory.
A red-colored row indicates that the previous row and the red row are not consecutive. This means that there is a gap in the collected trace data, for example because trace data has been lost due to an overflow.
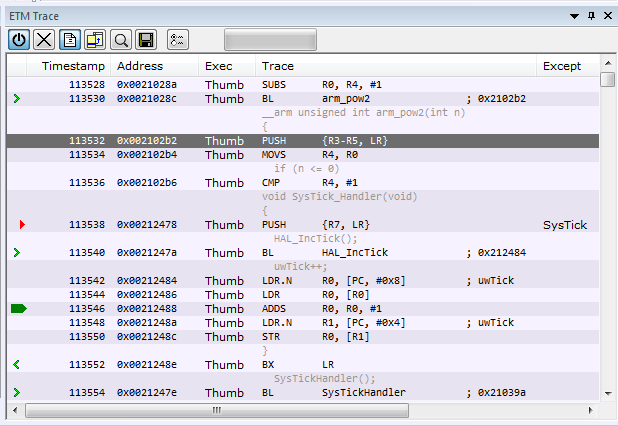
Display area (for ETM trace in the C-SPY hardware debugger drivers)
This area displays a collected sequence of executed machine instructions and other trace data.
Data trace is only available for the C-SPY I-jet driver or CMSIS-DAP driver, when using Arm7/Arm9/Arm11-based devices with ETM data trace.
This area contains these columns. Note that some columns depend on the C-SPY driver, the CPU, and the probe you are using.
The leftmost column contains identifying icons to simplify navigation within the buffer:

The yellow diamond indicates the trace execution point, marking when target execution has started.

The right green arrow indicates a call instruction.

The left green arrow indicates a return instruction.

The dark green bookmark indicates a navigation bookmark.

The red arrow indicates an interrupt.

The violet bar indicates the results of a search.
- Timestamp
The internal I-jet Trace timestamp.
- Address
The address of the instruction associated with the trace frame.
- Opcode
The operation code of the instruction associated with the trace frame. After the hexadecimal value, extra information can be displayed:
x2— if two instructions were executedC— if the instruction was read from the I-Cache
- Exec
The execution mode—
Arm,Thumb, orNoExec.
- Trace
The collected sequence of executed machine instructions. Optionally, the corresponding source code can also be displayed.
- Except
The type of exception, when it occurs.
- Access
The access type of the instruction associated with the trace frame.
DMAstands for DMA transfer. The address and data information shows which transfer that was performed.
- Data address
The data trace address.
- Data value
The data trace value.
- Comment
Additional information.
A red-colored row indicates that the previous row and the red row are not consecutive. This means that there is a gap in the collected trace data, for example because trace data has been lost due to an overflow.
Display area (for SWO trace)
This area contains these columns for SWO trace:
- SWO Packet
The contents of the captured SWO packet, displayed as a hexadecimal value.
- Cycles
The approximate number of cycles from the start of the execution until the event.
For J-Link, this number is reported by the CPU.
For I-jet, this number corresponds to the internal I-jet Trace timestamp.
- Event
The event type of the captured SWO packet. If the column displays
Overflow, the data packet could not be sent, because too many SWO features use the SWO channel at the same time. To decrease the amount of transmissions on the communication channel, point at the SWO button—on the IDE main window toolbar—with the mouse pointer to get detailed tooltip information about which C-SPY features that have requested trace data generation. Disable some of the features.
- Value
The event value, if any.
- Trace
If the event is a sampled
PCvalue, the disassembled instruction is displayed in this column. Optionally, the corresponding source code can also be displayed.
- Comment
Additional information, including the values of the selected Trace Events counters, or the number of the comparator (hardware breakpoint) used for the Data Log breakpoint.
A red-colored row indicates that the previous row and the red row are not consecutive. This means that there is a gap in the collected trace data, for example because trace data has been lost due to an overflow.
Tip
If the display area seems to show garbage, make sure you specified a correct value for the CPU clock in the SWO Configuration dialog box.
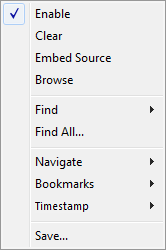
Context menu
This context menu is available:
Note
The contents of this menu are dynamic and depend on which features that your combination of software and hardware supports. However, the list of menu commands below is complete and covers all possible commands. Note that the shortcuts to the submenu commands do not use the Ctrl key.
These commands are available:
- Enable
Enables and disables collecting and viewing trace data in this window.
- Clear
Clears the trace buffer. Both the Trace window and the Function Trace window are cleared.
- Embed source
Toggles the Trace column between showing only disassembly or disassembly together with the corresponding source code.
- Browse
Toggles browse mode on or off for a selected item in the Trace window, see Browsing through trace data.
- Find>Find (F)
Displays a dialog box where you can perform a search in the Trace window, see Find in Trace dialog box. The contents of the window will scroll to display the first match.
- Find>Find Next (G)
Finds the next occurrence of the specified string.
- Find>Find Previous (Shift+G)
Finds the previous occurrence of the specified string.
- Find>Clear (Shift+F)
Removes all search highlighting in the window.
- Find All
Displays a dialog box where you can perform a search in the Trace window, see Find in Trace dialog box. The search results are displayed in the Find in Trace window—available by choosing the View>Messages command, see Find in Trace window.
- Navigate>After Current Loop (L)
Identifies the selected program counter and scans the trace data forward, collecting program counters, until it finds the same address again. It has now detected a loop. (Loops longer than 1000 instructions are not detected.) Then it navigates forward until it finds a program counter that is not part of the collected set. This is useful for navigating out of many iterations of an idle or polling loop.
- Navigate>Before Current Loop (Shift+L)
Behaves as After Current Loop, but navigates backward out of the loop.
- Navigate>After Current Function (U)
Navigates to the next unmatched return instruction. This is similar to stepping out of the current function.
- Navigate>Before Current Function (Shift+U)
Navigates to the closest previous unmatched call instruction.
- Navigate>Next Statement (S)
Navigates to the next instruction that belongs to a different C statement than the starting point. It skips function calls, i.e. it tries to reach the next statement in the starting frame.
- Navigate>Previous Statement (Shift+S)
Behaves as Next statement, but navigates backward to the closest previous different C statement.
- Navigate>Next on Same Address (A)
Navigates to the next instance of the starting program counter address, typically to the next iteration of a loop.
- Navigate>Previous on Same Address (Shift+A)
Navigates to the closest previous instance of the starting program counter address.
- Navigate>Next Interrupt (I)
Navigates to the next interrupt entry. (To then find the matching interrupt exit, follow up with After Current Function.)
- Navigate>Previous Interrupt (Shift+I)
Navigates to the closest previous interrupt entry.
- Navigate>Next Execution Start Point (E)
Navigates to the next point where the CPU was started, for example places where the application stopped at breakpoints, or was stepped.
- Navigate>Previous Execution Start Point (Shift+E)
Navigates to the closest previous point where the CPU was started.
- Navigate>Next Discontinuity (D)
Navigates to the next discontinuity in the trace data.
- Navigate>Previous Discontinuity (Shift+D)
Navigates to the closest previous discontinuity in the trace data.
- Bookmarks>Toggle (+)
Adds a new navigation bookmark or removes an existing bookmark.
- Bookmarks>Goto Next (B)
Navigates to the next navigation bookmark.
- Bookmarks>Goto Previous (Shift+B)
Navigates to the closest previous navigation bookmark.
- Bookmarks>Clear All
Removes all navigation bookmarks.
- Bookmarks>location (0–9)
At the bottom of the submenu, the ten most recently defined bookmarks are listed, with a shortcut key each from 0–9.
- Timestamp>Set as Zero Point (Z)
Sets the selected row as a reference “zero” point in the collected sequence of trace data. The count of rows in the Trace window will show this row as
0and recalculate the timestamps of all other rows in relation to this timestamp.
- Timestamp>Go to Zero Point (Shift+Z)
Navigates to the reference “zero” point in the collected sequence of trace data (if you have set one).
- Timestamp>Clear Zero Point
Removes the reference “zero” point from the trace data and restores the original timestamps of all rows.
- Save
In the ETM Trace and SWO Trace windows, this button displays the Trace Save dialog box, see Trace Save dialog box.
In the C-SPY I-jet driver and in the C-SPY simulator, this button displays a standard Save As dialog box where you can save the collected trace data to a text file, with tab-separated columns.